The consensus of seven institutions at home and abroad: CAR-T-induced CRS requires differentiated management methods, and consistent "grass-cutting" treatment may usher in new changes丨Yi Mai Meng broke the news
At present, CAR-T cell immunotherapy, as an emerging immunotherapy in recent years, has achieved significant effects in hematological tumors, but the toxic side effects have largely limited the wide application of CAR-T cells, especially cytokine release synthesis. Sign (CRS).
Although the FDA's approval regulations have standard management methods for CRS, and according to the real world data released by Novartis and Gilead at ASH 2019 last year, the incidence of CAR-T side effects is better than experimental data. However, a series of side effects such as CRS is still a major factor limiting the development of CAR-T cells. Recently, Professor Han Weidong, Professor Liang Aibin, and Professor Qian Wenbin are the corresponding authors. In an article jointly completed by seven institutions at home and abroad, it is proposed that CAR-T cells treat leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (B-NHL) The mechanisms that cause CRS are different, and it is proposed that the management of CRS should be subdivided for different tumor types and CAR-T treatment stages. The article was published in Nature's magazine Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (STTT).

▲ Image Source: nature
Partial CRS
In this study, the researchers proposed that compared with other hematological malignancies (for example) B lymphocytic leukemia, B-NHL has unique pathophysiological characteristics and clinical manifestations. The most obvious difference is that the lesion site of B-NHL is usually It is local.
Especially in patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy, local inflammation can be observed, manifested as local lymphoma or redness, swelling and major around the lesion. In order to distinguish it from systemic CRS (S-CRS), the study The team defined this local inflammatory response as local CRS (L-CRS).
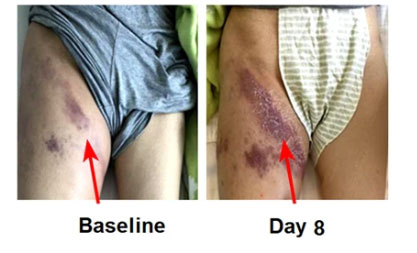
Local inflammation in B-NHL patients receiving CAR-T cells(Image Source: nature)
In fact, L-CRS has been reported long ago, but due to the lack of more examples, it did not have a big impact. L-CRS only occurs in interventricular tumors. For B-NHL, obvious L-CRS is not often observed, because before CAR-T treatment, these patients are usually given chemotherapy to reduce the tumor burden, even in Patients with such large tumor masses were excluded from the experiment.
But in clinical trials conducted by Han Weidong's team, patients with large tumor masses often observed obvious L-CRS. At the same time, L-CRS is the earliest adverse event (AE) observed in B-NHL patients after receiving CAR-T therapy. It usually occurs within 0-5 days after CAR-T cell infusion. During this period, systemic events may also occur. Sexual CRS (S-CRS).
Although the occurrence of L-CRS is necessary for the efficacy of CAR-T, S-CRS can lead to more serious consequences. Therefore, timely control of L-CRS helps prevent severe S-CRS. The research team found in early clinical trials that IL-6 blocking antibodies could not effectively alleviate the L-CRS response, but aggravated the L-CRS response. This indicates that the underlying mechanism of L-CRS may be specific.
A model: the occurrence and progress of CRS
Therefore, the research team believes that the mechanisms of CAR-T cell therapy for leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (B-NHL) caused CRS are different, and it is necessary to distinguish between differences in judgment and treatment clinically. However, at present, there is no difference between the two CRS management methods, and even some management recommendations are not fully applicable to B-NHL patients.
For this reason, Han Weidong’s team tentatively proposed a new model based on the underlying biological process and the pathophysiological mechanism of inhibition to simulate the occurrence and progression of CRS during CAR-T cell therapy in B-NHL to help Researchers and clinicians have a better understanding of the basic biological principles of CRS in order to understand and manage CRS more reasonably.
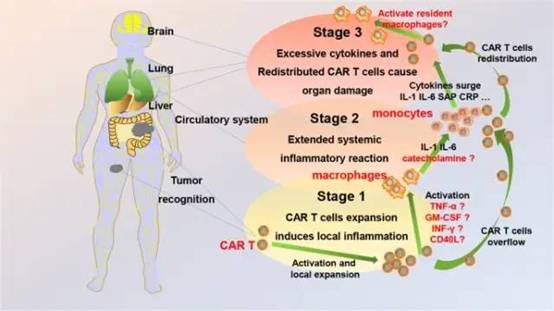
▲ CRS research model(Image Source:nature)
The research team divided the development of CRS caused by CAR-T cells in B-NHL patients into four stages: (1) CAR-T cell local expansion; (2) CAR-T cell overflow and inflammatory cytokine surge; (3) Redistribution of CAR-T cells and organ damage stage; (4) Recovery stage. In this model, tumor burden and bone marrow suppression (BMS) are considered to be determinants of CRS.
At the same time, this article was written by Professor Han Weidong, Professor Liang Aibin, and Professor Qian Wenbin as the corresponding authors. It took two years to complete this article by seven institutions at home and abroad, with a high degree of consensus.
The next goal: segmented management
Aiming at the current undifferentiated management method of CRS caused by CAR-T cell therapy, the Han Weidong team is working with many institutions to draft detailed identification indicators and treatment plans for each stage of the four processes of CAR-T cell induction of CRS.To ensure that even a large tumor burden does not cause severe CRS of grade 4 to occur, implement the guiding ideology of prevention first and control second.
Article source: Yimai Ke News MedClub News